Amazon (mkt cap ~$760B) recently paid more for Whole Foods ($13.7B) than the balance sheets of many mid-market grocers. This frames the obvious question for all grocers: how can your business compete long-term?
This is an especially challenging question for the smaller-cap grocers. Large companies such as Walmart (mkt cap ~$250B) and Target (mkt cap ~$40B) can afford sizable investments. To a lesser degree, the balance sheets of the next tier of grocers, like Kroger (mkt cap ~$21B), also allow them to focus on a couple of key moves and a few smaller initiatives, and to double-down if necessary.
Smaller grocery chains have to look more carefully, however. Except for mergers or sales, their balance sheets are not strong enough to complete large transactions on their own. Nor do they have the operating margin to buy with debt without materially impacting their P&Ls and carrying long-term risk to pay it down, especially if the economy takes a downward turn. With average pre-tax profits of 2% and an annual growth of 0.9% (2012-17), retained earnings can barely meet working capital growth needs, leaving limited capital for innovation.[i]
Mid-Market Innovation
Capital availability aside, the main question still remains: what should mid-market grocers do? To answer this question, let’s break it down into smaller questions and then explore those topics:
1. Without active strategic steps, can mid-market grocers survive over the next 1-2 decades? Do they have to counteract Amazon’s thrust and make similar moves to stay in business? Will they be weaker if they cannot or do not do so?
2. If they act, how should they proceed? Diversify into new markets? Consolidate with other mid-sized grocers? Or try to sell to Amazon, Walmart or Target assuming they are interested?
3. Or, should they build their own path by seeding and growing innovation, and grafting small acquisitions to accelerate growth and achieve scale down these paths?
Long-term Survival
The US grocery retail market stands at $649B today, with 3.4M (1% of the US population) employees across the 66,000+ businesses comprising this industry.[ii] Given a growing population and the fact that in times good or bad, we all must eat, demand for food is unlikely to go down, though there may be shifts in preferences (e.g., generics v. branded) depending on economic conditions.
In other words, the industry is not small, not consolidated, and not at risk for a decline in demand. Rather, it is large, fragmented, and diverse, with fundamentally stable or growing demand. This makes it difficult for disrupters to disrupt broadly or deeply, and for adaptive innovators, it presents many options.
Evolution favors innovation and adaptability over size and scale, and nature provides useful insight into this Darwinian paradigm. While size and scale produce advantages for certain species, it is no guarantee of future success- it is a sign of successful growth, of successful past innovation. Colossal dinosaurs once dominated the planet, but the reason they rose to prominence, and the only reason their lineage persists in birds is because of adaptive innovations.
With the universal need for food, severe consolidation of grocery chains is unlikely as long as the US economy grows. And with the diversity of ecosystem players, customer preferences, and products, those who innovatively adapt will continue to grow.
Capital: Strength or Weakness?
For over a decade now, Amazon has taken advantage of its strong balance sheets and scale to gain presence in groceries. Given that Amazon’s market cap is roughly twice that of Target’s and Walmart’s combined is a material factor in its choice of strategic weapon: capital. Amazon’s investments related to grocery retailing are approximately $15B.
However, it is incorrect to assume that lots of capital means inevitable success. Many acquisitions simply fail to take root in their new home, no matter how useful the innovation. And companies such as Webvan failed under the weight of their capital because they failed to establish product-market fit incrementally and left no room for adaptive course-correction.
How to Proceed?
If Darwinism tends to prevail, then capital is not an unequivocal advantage, and the existential factor is adaptive growth, not survival.
We believe the multi-part answer is to (1) seed the eco-system for knowledge and initial product-market validation, (2) place 1-2 larger bets (at any given time for focus) based on an understanding of the market forces towards new business models or diversification, then (3) strengthen them to achieve scale, and (4) in parallel, carve out or sunset lines of business with the strongest headwinds to free up cash and focus on growth.
The outcome of such steps can put a mid-market grocer into high-growth business(es) that may not collide directly with Amazon or Walmart, and possibly even set the stage for a valuable acquisition or merger.
Topline Levers
Across these phases – seeding the ecosystem, placing 1-2 larger bets, and achieving scale – the two topline levers are greater share of wallet and new customers. These can come from new products and services.
Products (“SKUs”) such as staples and provisions, non-perishables, and fresh fruits & vegetables, all offer room for expansion. Depending on local demographics, preferences such as branded vs. non-branded, price vs. selection, organic foods, local produce, regional/ethnic items, and specialty items such as liquor and wine, define growth options.
SKU expansion does not require significant capital. Rather it requires a process that allows select experiments to be managed by the grocer, and a much longer ‘tail’ to be ‘self-managed’ by the SKU suppliers, where the grocer only provides limited ‘shelf space’ for a limited time (e.g., in-store endcaps or online kiosks) and charges for the service (and is able to do it without losing money). It is reasonable for SKU suppliers to be willing to pay for more visible use of physical space, differentiated presentation, or better ways to engage customers.
Online shopping enables choice extensions and endless aisles at a modest cost, whereas in-store options can emphasize experience. Demographic understanding of customer needs (healthy foods, organics, specialty foods, local/seasonal produce, etc.) can be assessed through affinity programs and community engagement combined with analytics. Going beyond food and provisions, adjacent businesses such as banking kiosks or medical ‘minute clinics’ can be evaluated in the same way.
Services such as partially- or pre-cooked foods, cellar management (a la VinCellar), produce delivery (a la Instacart or Peapod), meal delivery (a la Blue Apron), in-store eateries, and in-store convenient checkout without PoS lines can also be offered without material investment as vendor or partner offerings from established players and startups.
Bottomline Levers
The main bottomline levers are operational expenses such as rent, labor, and logistics including warehousing and supply chain management (e.g., inventory turns, lower margin items online); and financial items such as cash flow management or cost of debt. Many optimizations for these levers (e.g., robotic warehouses, robotic kitchen management, blockchain-based cold chain tracking, etc.) can also be enabled by partnerships with technology-based startups.
Capital Efficiency
In reviewing the above ideas, it becomes clear that many options are available in capital-efficient ways. Among these options, relationships with venture firms can facilitate access to both topline and bottomline tech-based innovation partners.
We are in an era of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), which itself mitigates capex. Examples of services include online store builders and marketplaces (e-tail), security, brand/user preference analysis and brand promotion (martech, AI), customer service platforms (chatbots, CRM, KPO), and fleet management (IoT, gig economy apps). As federated web services with APIs, integration of SaaS offerings with the grocer’s enterprise software has become less expensive. With responsive design techniques, consistent desktop and mobile presentations for omni-channel access have become easy. And with integrated dev-ops processes, their deployment and upgrades have become easier as well.
Similarly, the gig economy mitigates capex and opex. Alternatives to home delivery by Whole Foods or Walmart Grocery (earlier known as Walmart-to-Go) can be made available without capex through third parties such as Instacart and Peapod. Federated independent couriers (e.g., Dispatch[iii])provide alternatives (figure 2). Also on the innovation frontier, though groceries are not the prime use case today, third-party drone companies offer drone-based services for commercial payloads of various sizes and type.
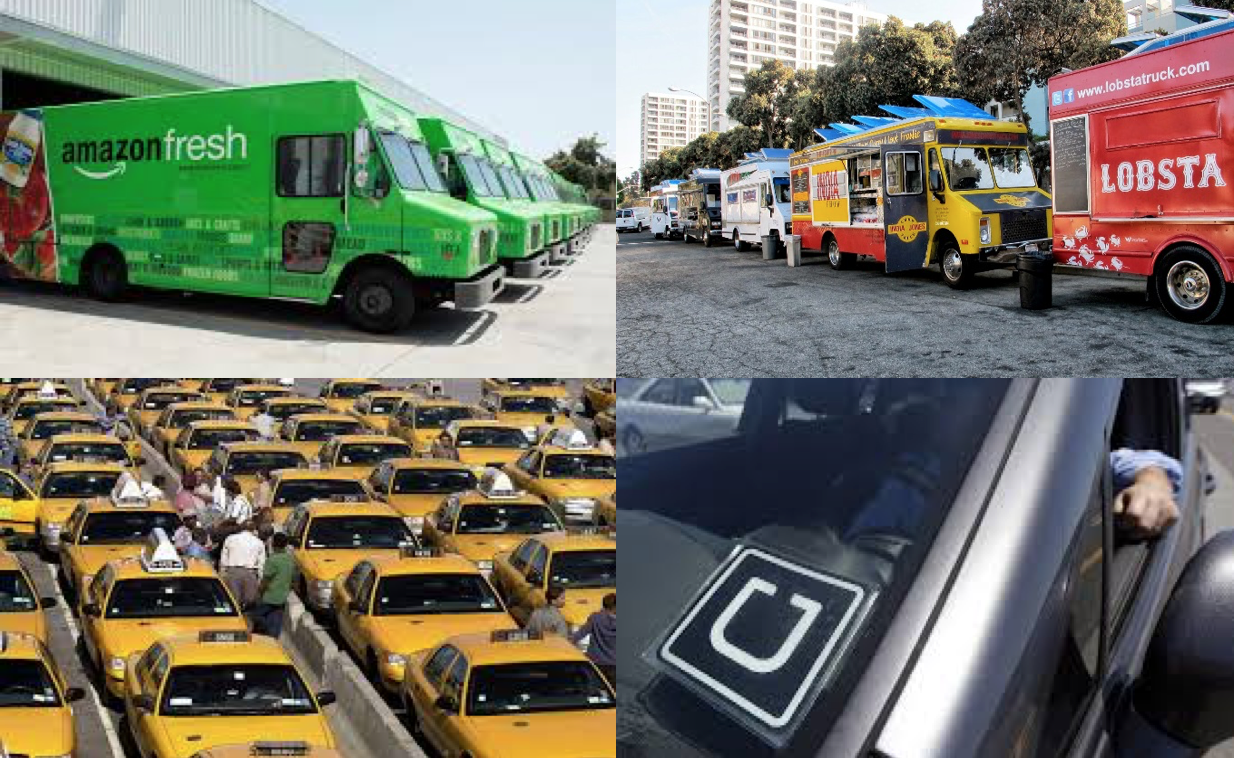

Figure 2. Which is better – owned delivery fleets, or independents marshalled with SaaS software? The answer may lie in the clash of medallions vs. Uber.
All of these services become easier to procure through relationships with VC firms that have a high awareness of these start-ups and use cases. The VC community has been quite active in grocery-focused investments. With 100+ investments, ~429 investors, and ~47 exits, grocery-focused VC firms have been active globally. Driving growth through capital-efficient innovation is necessary for mid-market grocers to stay competitive in the industry. Venture firms can provide options for adaptation, intelligence and diversification without billion-dollar expenditures.
[i] http://www.mngrocers.com/index.php/industry/stats
[ii]https://retailowner.com/Benchmarks/Food-and-Beverage-Stores/Supermarkets-Grocery-Stores#290291-profit
[iii] Dispatch is a Great North Labs investment